Glutamine, an amino acid, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, cell division, and immune function. Learn about its benefits, sources, and how supplementation for bodybuilders can support muscle recovery, immune support, and gut health. Find out which foods naturally contain this amino acid and when supplementation may be necessary.
Key Takeaways
- Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the body and is commonly found in proteins.
- It plays a vital role in protein synthesis, cell division, and immune function.
- Involved in the transport of nitrogen between tissues and organs, it's an important energy source for cells, especially in the intestine and immune cells.
- Essential for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier and regulating acid-base balance.
- Supplementation has been studied for potential benefits in muscle wasting, immune support, and gut health.
- Athletes and bodybuilders commonly use it to support muscle recovery and growth.
- Naturally present in foods like meat, fish, dairy products, and certain plant-based sources.
- In certain conditions, the body's demand for glutamine may exceed its ability to produce it, leading to a potential deficiency.
- Generally safe when taken in appropriate doses, but high doses may cause gastrointestinal side effects.
- Consultation with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen is essential.
Overview

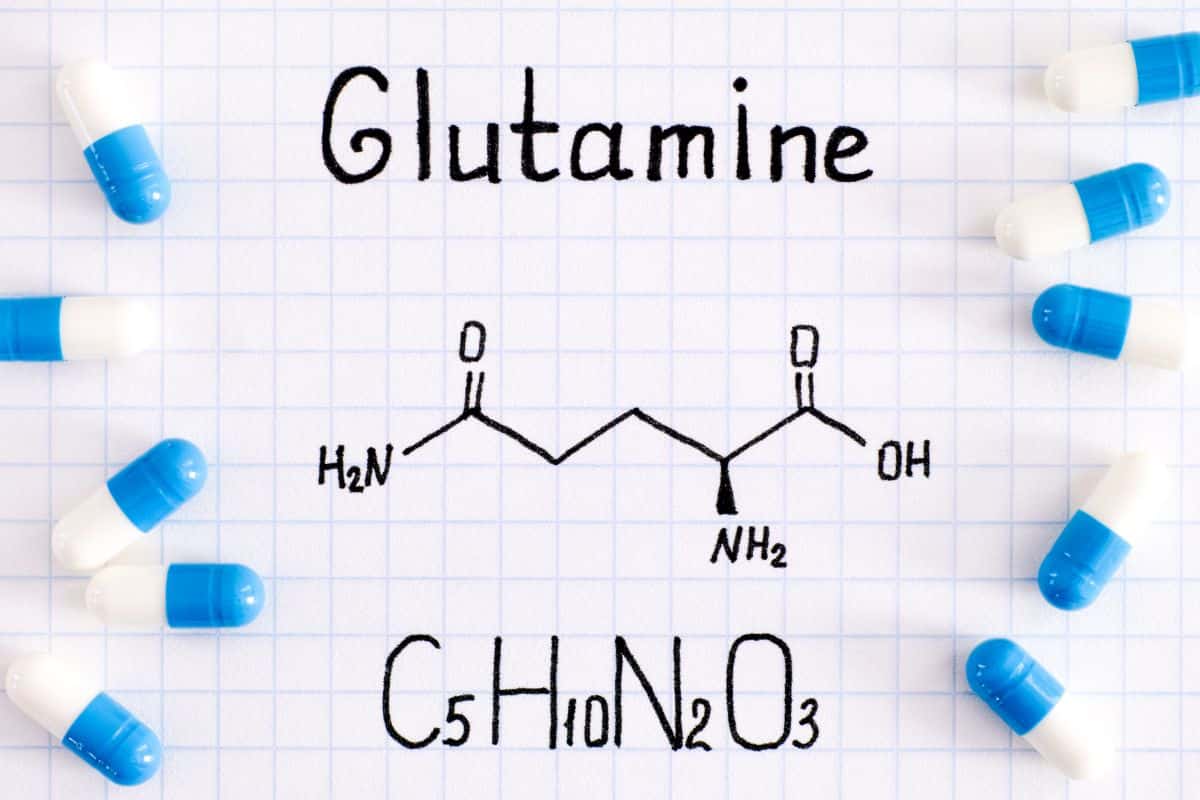
Glutamine is a vital amino acid that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. As the most abundant amino acid found in proteins, it's classified as a polar amino acid with a neutral side chain charge. Its unique structure includes an amide group and a carboxylic acid group.
Classification
Glutamine's classification as a polar amino acid with a neutral side chain charge makes it an essential component for protein synthesis, cell division, and immune function. This amino acid is involved in the transport of nitrogen between tissues and organs, which is crucial for maintaining optimal bodily functions.
Role in the Body
Glutamine serves as a vital energy source for cells, especially in the intestine and immune cells. It is also responsible for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, which is essential for gut health. Additionally, it plays a significant role in regulating the acid-base balance within the body, ensuring optimal pH levels.
Furthermore, supplementation has garnered attention for its potential benefits in various conditions, including muscle wasting, immune support, and gut health. Athletes and bodybuilders commonly utilise it to support muscle recovery and growth.
While glutamine is naturally present in many foods, the body may not always produce enough to meet the demand, especially during periods of illness or intense exercise. In such cases, supplementation may be necessary to prevent potential deficiencies.
It is important to note that glutamine is generally considered safe for most individuals when taken in appropriate doses. However, high doses may lead to gastrointestinal side effects. As with any supplementation regimen, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating it into your routine.
Benefits

Glutamine offers a wide range of benefits that can positively impact overall health and well-being. From protein synthesis to immune function, this amino acid plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the body.
Protein Synthesis and Muscle Recovery
One of the key benefits of glutamine is its role as a muscle building supplement. It provides the necessary building blocks for the synthesis of proteins, which are crucial for muscle growth and repair. Supplementing with glutamine can help replenish the body's stores and support muscle recovery, allowing individuals to bounce back faster from strenuous workouts and reduce muscle soreness.
Immune Function and Support
Glutamine also plays a vital role in supporting immune function. It is an important energy source for immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages, which are responsible for fighting off infections and diseases.
Intestinal Health and Barrier Integrity
Maintaining a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being, and glutamine plays a significant role in supporting intestinal health. It is essential for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, which acts as a protective barrier against harmful substances and pathogens.
Regulation of Acid-Base Balance
Maintaining the right balance of acids and bases in the body is crucial for optimal health. Glutamine plays a role in regulating acid-base balance by acting as a buffer. It helps neutralise excess acid in the body, preventing imbalances that can lead to various health issues.
Food Sources
Meat and Poultry
Meat and poultry are excellent sources of glutamine. These include beef, chicken, turkey, and pork. These animal-based protein sources not only provide glutamine but also contain other essential amino acids necessary for overall health and muscle growth.
Fish and Seafood
Fish and seafood are another great source of glutamine. Varieties such as salmon, tuna, cod, and shrimp are not only rich in this amino acid but also provide omega-3 fatty acids, which have numerous health benefits.
Dairy Products
Dairy products, including milk, yogurt, and cheese, are also good sources of glutamine. These products not only offer a convenient way to incorporate it into your diet but also provide calcium and other essential nutrients for bone health.
Plant-Based Sources
For those following a plant-based or vegetarian diet, there are several plant-based sources of glutamine. Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are rich in it and provide a good amount of dietary fiber as well. Additionally, certain grains and seeds, including quinoa, brown rice, and pumpkin seeds, are also good sources.
Endogenous Production and Deficiency
What are the potential side effects of glutamine supplementation?
High doses of glutamine may cause gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. It is crucial to follow the recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional to minimise the risk of side effects.
How does glutamine support muscle recovery?
Glutamine plays a key role in protein synthesis and provides the necessary building blocks for muscle growth and repair. During intense exercise, the body's demand for glutamine increases, and supplementation can help replenish stores, support muscle recovery, and reduce muscle soreness.
How does glutamine support immune function?
Glutamine serves as an important energy source for immune cells and is involved in the transport of nitrogen, which is crucial for optimal immune function. Adequate levels of glutamine can help ensure that the immune system operates effectively, reducing the risk of illness.
How does glutamine support gut health?
Glutamine is essential for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier and supports the growth and repair of the intestinal lining. It helps strengthen the intestinal barrier and promotes the production of mucin, a substance that forms a protective layer on the intestinal lining, reducing the risk of gut-related issues.
How does glutamine regulate acid-base balance?
Glutamine plays a role in regulating acid-base balance by acting as a buffer. It helps neutralise excess acid in the body, preventing imbalances that can lead to health issues. By supporting acid-base balance, glutamine helps maintain proper pH levels in the body.
Conclusion
L-Glutamine is a vital amino acid that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within the human body. From supporting protein synthesis and immune function to aiding in muscle recovery and gut health, L-Glutamine is essential for maintaining overall well-being.
While it is naturally present in many foods and produced by the body, supplementation may be necessary in certain situations to prevent potential deficiencies. It is generally considered safe when taken in appropriate doses, but consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to ensure proper usage and to address any potential concerns.
Understanding the importance of L-Glutamine and its potential benefits can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and fitness goals. Whether through dietary sources or supplementation, L-Glutamine can be a valuable addition to support overall health and well-being.
By considering the unique functions and benefits of L-Glutamine, individuals can take proactive steps to support their health and achieve their personal goals. With proper guidance and consideration, L-Glutamine can be a valuable asset in promoting optimal health and wellness.